What is secure boot in BIOS?
We explain what Secure Boot is and what it is for. In addition, we briefly talked about its implications when installing operating systems on a computer.

We are going to explain what Secure Boot is and what it is for. Most likely, you have heard or read about this functionality on your motherboard, especially if you like to install alternative operating systems to Windows. In this guide you will find all the information you need.
Don’t forget that Secure Boot is built into the BIOS or, its most recent version, UEFI. Therefore, you will have to go to it to configure this function step by step, in a similar way to when you want to boot your computer from a USB. With this in mind, it is time to start solving doubts regarding this protection.
What is BIOS and UEFI?
Before talking about Secure Boot, it is interesting that we make some clarifications. Therefore, let us explain what BIOS and UEFI are, since Secure Boot is strictly related to both concepts.
BIOS is an acronym for Basic Input Output System. It appears for the first time back in 1975 and its main function is to initialize all the components of the computer and launch the operating system. BIOS has an infinite number of basic parameters that influence the behavior of the different hardware elements.
In short, it is a very simple software, integrated into the motherboard, which runs before the installed operating system and has a great impact on the behavior of the computer.
For its part, UEFI is the acronym for Unified Extensible Firmware Interface. Again, we are talking about a firmware that is installed on the motherboard and is responsible for starting the equipment. It was created in 2002 by Intel and has some more modern features, such as the ability to use the mouse to access the different menus. However, in reality its main functions are identical to those of BIOS.
What is Secure Boot and what is it for?
If you have read the previous section, you already know that your motherboard has its own operating system, called in this case firmware, with options that modify the behavior of the computer and the main hardware components. One of those settings is Secure Boot, the feature at hand in this guide.
Secure Boot, also known as secure boot, is a UEFI feature that came from Windows 8. It is a protection that prevents any system that is not certified or signed from running.
It is clear that this is very interesting protection when it comes to protecting your computer from malware. Because? Because it is located in the BIOS or UEFI, prevention occurs long before the malicious code has been executed. In this way, we say that this is an early security measure, very different from what Smart Screen or an antivirus would be, which run on top of the operating system.
What is not Secure Boot?
It is important to answer this question. Historically, this security measure has generated controversy, especially among the Linux community. The reason is that some distributions are not signed and therefore cannot be installed while keeping Secure Boot enabled. First you have to disable the protection and then install the Linux distribution.
It’s clear that Secure Boot is really there for security and not as a monopoly measure by Microsoft. We are not saying it, but the Debian team itself, an institution in the Linux world. Currently, the most important Linux distributions support Secure Boot, that is, they are signed as legitimate. These are some of the ones you can install on your computer:
- Ubuntu
- Red Hat
- Fedora
- SUSE
- Debian
Even alternative operating systems, like Chrome OS Flex, are signed and support this layer of security. Does this mean that operating systems that are not certified for Secure Boot cannot be installed?
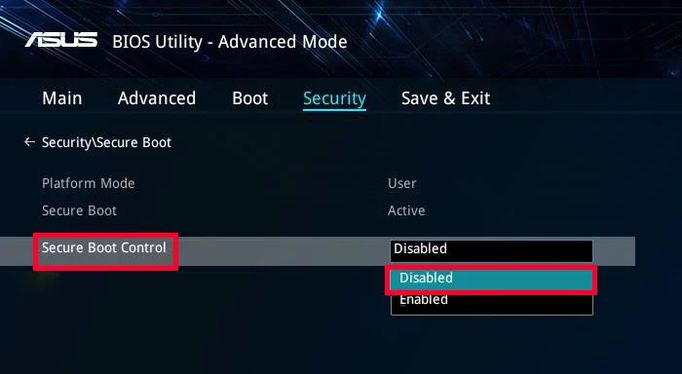
How to disable Secure Boot?
Secure Boot is not a permanent feature. The truth is that it can be deactivated relatively easily. Thus, you will be able to install any software on your PC, even if it has not been signed by Microsoft. Just enter the UEFI BIOS settings of your computer and locate the Secure Boot setting.